Exosome booster can enhance the ability of cells to secrete exosomes and it was expressed in HEK293T by lentiviral vector to verify its function. The experiments includes three parts: the transfection effect of exosome booster was detected by an inverted fluorescence microscope. The presence of exosome was detected by electron microscopy and the effect of exosome booster on the exosome secretion of HEK293T was detected by NTA analysis.
Exosome-booster stable cell line construction
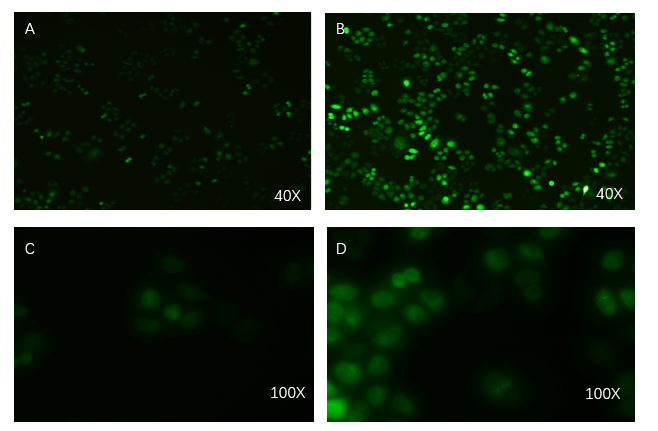
PCDH plasmid with exosome booster and CopGFP reporting system was transfected into HEK293T cells stably, and fluorescence before and after transfection was detected by inverted fluorescence microscopy. Figure A is the HEK293T cells of the untransformed plasmid, while figure B is the HEK293T cells of the transformed exosome booster. It can be observed that transfected cells can be stimulated to produce intense fluorescence. Figure. C and D were the fluorescence images of the control group at 100 times (figure. C) and the experimental group (figure. D).
Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) detection
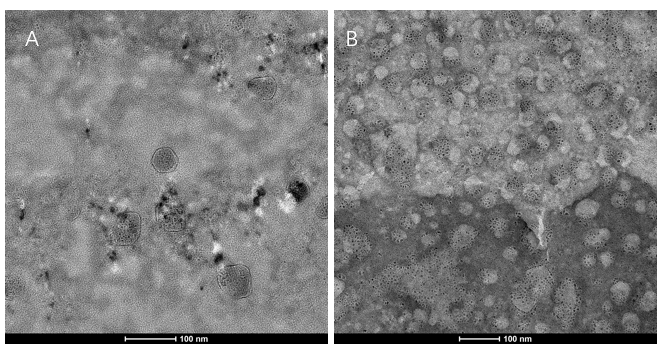
We extracted exosomes from HEK293T cell and negatively stained it with phosphotungstic acid. Subsequently, we use TEM to detect it in 100nm . The experimental results demonstrated that HEK293T expressed exosome booster genes (figure B) could dramatically increase its exosome secretion compare with control cell (figure A)
NTA analysis
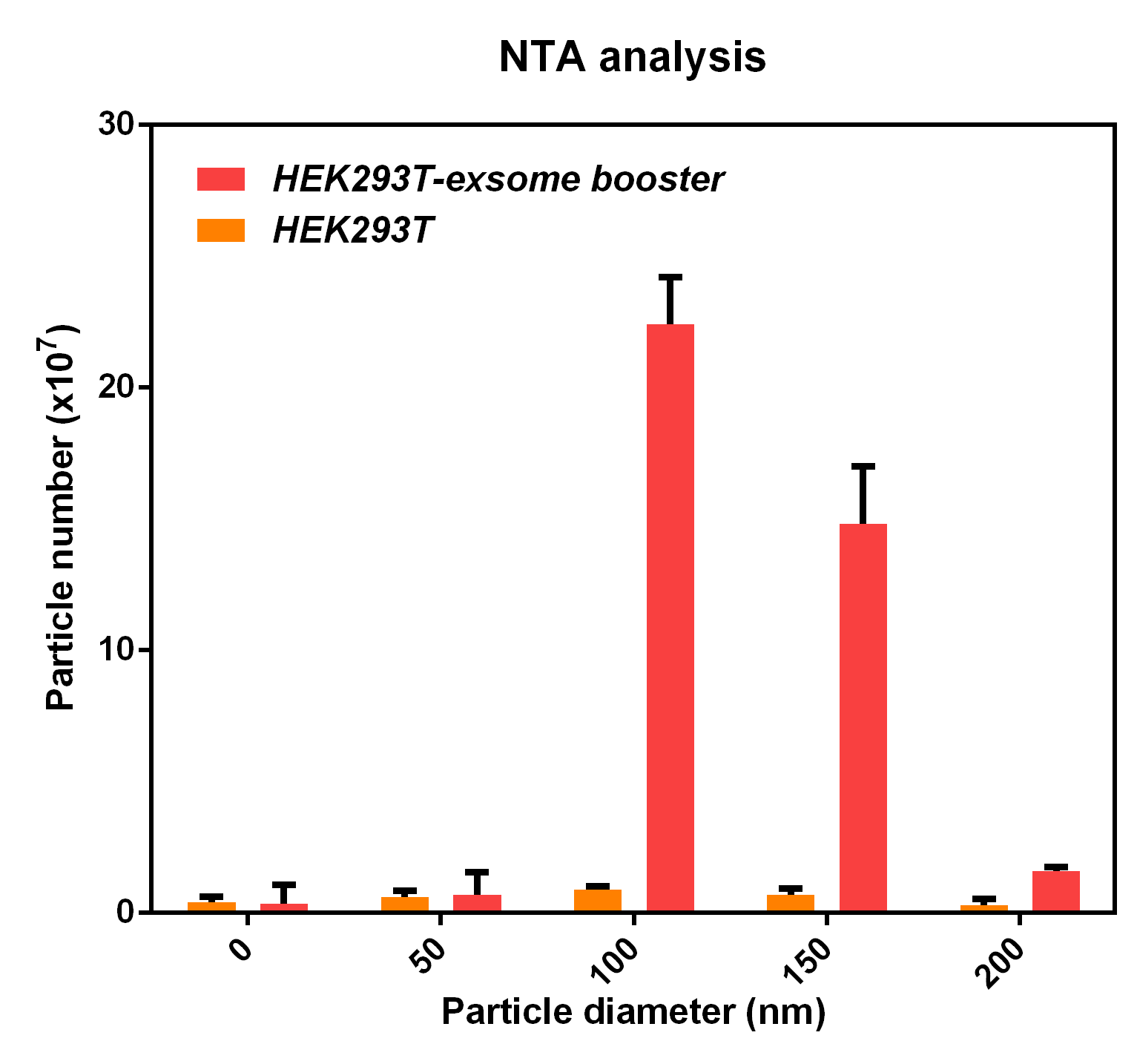
The NTA analysis refers to the nanoparticle tracking analysis. The experimental results showed that HEK293T cell overexpressing exosome booster had significantly higher granules numbers at 100nm and 250nm than the control cell (about 23 times as much as the control cell). This indicates that exosome booster can increase the number of exosomes secreted by 293T cell.
Exosome uptake experiments
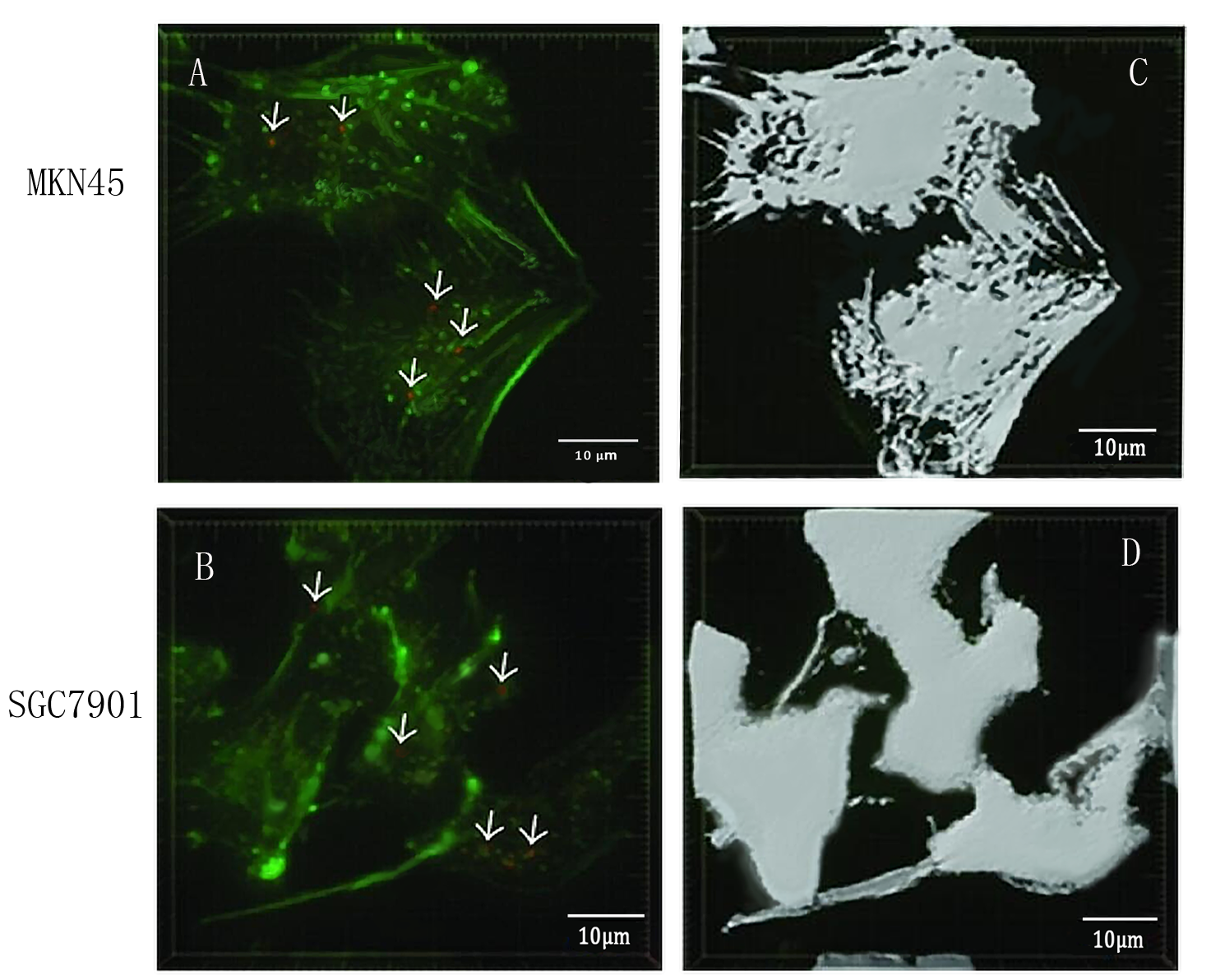
To detect whether exosomes whether could enter gastric cancer cells,we used confocal microscopy to observe the uptake of gastric cancer cells MKN45 and SGC7901 with exosomes . First, exosomes were extracted from 293T cells and stained with PKH26 exosomes (red fluorescent dye). The MKN45 and SGC7901 cells were stained with a FITC dye. Exosomes and gastric cancer cells were incubated together for 6 hours. Subsequently, the uptake of exosomes by gastric cancer cells was examined by fluorescence confocal microscopy. Figure. A and C indicate that gastric cancer cells MKN45 and SGC7901 can ingested exosomes. Figure. B and D showed the cytoskeletal structures of MKN45 and SGC7901 in gastric cancer cells detected by β-tubulin antibody.
Applications of BBa_K2796028
User Reviews
UNIQfd65ad3200c1902d-partinfo-00000000-QINU
UNIQfd65ad3200c1902d-partinfo-00000001-QINU